A Comprehensive Guide on ISDN
Even if you aren’t that well-versed with telecommunication lexicon, you still might have come across a term—ISDN, which is the abbreviation for Integrated Services Digital Network.
It found its way into mainstream media and pop culture after Jon Postel, the legendary American computer scientist who made several important contributions to the development of the Internet, famously said: “But I do have a computer at home and a pretty good ISDN connection.”
What is ISDN?
ISDN is a circuit-switched telephone network system that transmits both data and voice over a digital line. In simple words, it is a set of communication standards to transmit data, voice, and signaling. .
But did you know that it is going to be phased out by 2025? In January 2020, BT Openreach announced its decision to stop or ‘switch off’ the ISDN and Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) service in December 2025.
In this blog post we will discuss everything about ISDN, starting from its origin and evolution to how it works, its pros and cons, and the alternatives. Read on to know more.
History and Evolution of ISDN
As the saying goes “Necessity is the mother of invention.” ISDN was created out of necessity as analog phone systems were unreliable for long-distance connections and the networks failed constantly.
Starting from the 1960s to late 70s, the core telephone system in the western countries began to change from analog to a packet-based, digital switching system. Telephony offices that connected through the public switched telephone network (PSTN) started using digital signals to transmit their voice and data.
The wires that connected users, however, were still analog and they were referred to as “the last mile.” But the transition laid the foundation stone for ISDN.
In 1980, work on the standard started at Bell Labs and was formally standardized in 1988 in the CCITT “Red Book”. That year, the UN-based International Telecommunications Union (ITU) began recommending ISDN as a new system to deliver data.
Just two years after that, the National ISDN 1 (N1-2) was rolled out. Following that, ISDN over Ethernet (ISDN-E) was launched. ISDN-E leverages Ethernet technology to deliver ISDN services over high-speed internet connections.
Additionally, advancements in digital networking standards have led to the introduction of Primary Rate Interface (PRI) ISDN, which offers higher capacity and more advanced features than Basic Rate Interface (BRI) ISDN. PRI ISDN is particularly well-suited for businesses with high call volumes and complex communication requirements.
After 2025, BT Openreach will stop selling ISDN at what’s known as the Stop Sell date and ISDN will be switched off completely. All phone lines in the UK would need to transition to a completely digital network. They need to route calls over Internet Protocol (IP) instead of traditional phone lines.
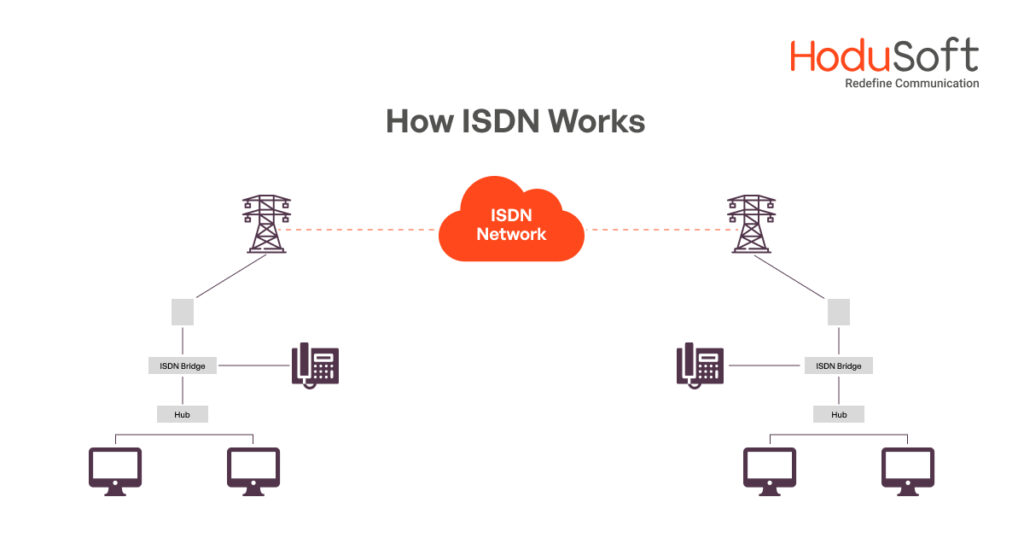
How Does ISDN Work?
Defining ISDN and knowing its history and evolution is one thing, but understanding how it operates is a different ball game altogether. Many individuals turn to ISDN for high-speed internet access when alternatives like DSL or cable modem connections are unavailable. Setting up ISDN typically involves collaboration with your Internet Service Provider (ISP), and much of the process can be managed conveniently from your own home. Here’s a basic rundown of how ISDN functions:
1. Connection via POTS Line
ISDN is typically connected through a traditional Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) line, allowing access to both phone numbers simultaneously. Before diving into the setup process, ensure you have a functional POTS line and assigned phone numbers ready to go.
2. Collaboration with ISP
Working in tandem with your ISP, you’ll commence the setup process. Your ISP will provide guidance and assistance throughout, ensuring a smooth transition to ISDN services.
3. Hardware Configuration
Once your POTS line and phone numbers are sorted, it’s time to configure the necessary hardware. This may involve installing terminal adapters or other equipment to facilitate communication between your devices and the ISDN network.
4. Voice and Data Configuration
With the hardware in place, you can proceed to configure your ISDN connection for both voice and data communications. This step may involve setting up voice services for phone calls and data services for internet access, depending on your specific needs and preferences.
5. Testing and Troubleshooting
After configuring your ISDN connection, it’s essential to conduct thorough testing to ensure everything is functioning as intended. This may involve making test phone calls, checking internet connectivity, and troubleshooting any issues that arise along the way.
6. Finalization and Activation
Once testing is complete and any issues have been addressed, your ISDN connection is ready for activation. Your ISP will finalize the setup process and activate your ISDN services, allowing you to enjoy high-speed internet access and reliable voice communication.
Advantages of ISDN
Now that we have a basic understanding of what ISDN is and how it works, let’s explore some of its key advantages:

1. Digital Clarity
What’s common between Belgian fashion designer Diane von Furstenberg and Canadian-American motivational speaker Brian Tracy? Their focus on clarity! The former famously said, “Clarity is the most important thing.” The latter quoted, “Clarity is essential.” That holds true for ISDN. It delivers clear, high-quality voice calls with minimal distortion.
2. Faster Data Transfer
Did you know that ISDN users can achieve data rates of up to 128 Kbps? ISDN offers a high data transfer rate due to its sophisticated digital architecture. That makes it ideal for tasks such as video conferencing, file transfers, and internet browsing.
3. Simultaneous Voice and Data
ISDN supports the simultaneous transmission of voice and data over the same line. Using ISDN, users can make phone calls while browsing the internet or sending or receiving faxes without experiencing any degradation in quality or speed.
4. Reliability
“Reliability is the precondition for trust.” Equipped with built-in error detection and correction mechanisms, which ensure data integrity, ISDN connections are highly reliable. This reliability is particularly crucial for businesses and organizations that depend on constant connectivity for their operations.
5. Scalability
ISDN is highly scalable. It enables users to increase or decrease the number of B channels as needed to accommodate changing demand. This scalability makes it suitable for businesses of all sizes starting from small stores to large enterprises.
6. Supports Wide Range of Value-Added Services
ISDN supports a wide range of value-added services, such as:
- Caller ID
- Call forwarding
- Call waiting
- Conference calling
These features enhance productivity and convenience for users while simplifying communication management.
7. Global Availability
ISDN is widely available in many countries around the world. That makes it a reliable choice for international communication. Its standardized protocols ensure interoperability between different ISDN networks.
8. Security
ISDN offers a wide range of security features, such as encryption and authentication. This is important for businesses handling confidential information or conducting secure transactions.
9. Multiple Digital Services
As ISDN channels have reliable connection, it is used to facilitate the user with multiple digital channels. With ISDN, users can establish multiple digital channels (known as B channels) on a single line. Each of the channels is capable of carrying data at speeds of up to 128 kbps.
Disadvantages of ISDN
While ISDN offers several advantages, it’s important to consider its drawbacks as well. Here are some of the disadvantages associated with ISDN:
1. Higher Cost
The cost of ISDN tends to be higher than some traditional broadband options. The expense of ISDN services, including installation, monthly fees, and usage charges, can be exorbitant for some users.
2. Competition from Advanced Technologies
Even though ISDN found a niche in industries like broadcasting and video conferencing, it struggled to keep pace with newer telephony technologies that continued to evolve and improve over time.
3. Migration Challenges
Switching from ISDN to alternative technologies can pose challenges for businesses with complex communication requirements or legacy systems built around ISDN infrastructure.
4. Dependency on Legacy Equipment
Many businesses that rely on ISDN invest heavily in legacy equipment and infrastructure that is incompatible with newer technologies. Upgrading or replacing this equipment to support alternative communication solutions can be costly and time-consuming.
5. Impending Phase Out
These demerits, along with the declining demand for ISDN services and widespread adoption of alternative technologies, have compelled telecom providers to phase out ISDN by 2025. It may come as shocking news to many, but ISDN is indeed going to be completely shut down by 2025.
Are Businesses Prepared For The Complete Shutdown of ISDN?
In 2020, BT announced that it will not sell new ISDN and PSTN and it aims to completely shut off both types of networks by 2025. It will replace ISDN and PSTN with IP (Internet Protocol) fiber-based network and infrastructure.
However, the most disturbing thing is a majority of businesses do not know about the news, let alone being prepared for the big switch.
A study published by Gamma Communications in collaboration with the Centre for Economics Business Research (Cebr) revealed that 30 percent of UK-based businesses are unaware about the news of ISDN being phased out by 2025.
Even though the switch-off has already started, 74 percent of businesses are yet to complete essential migration tasks. Almost half of businesses surveyed (49 percent to be precise) have not begun researching alternatives to ISDN and PSTN.
When it comes to awareness, businesses in urban regions display higher awareness than businesses in other regions. For instance, 59 percent of businesses in London know that ISDN would be completely phased out by 2025, whereas just 44 percent and 47 percent of businesses are aware of the shift in Northern Ireland and Southeast England, respectively.
As per experts, businesses that are still using ISDN and PSTN need to act now and explore various alternatives to both the networks so that they can have a seamless transition to modern solutions.
Alternatives to ISDN
With ISDN’s impending phase-out, businesses and individuals need to seek alternative solutions for their communication needs. Fortunately, here are some alternatives to ISDN that offer comparable or superior functionality.
1. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
VoIP technology allows for voice communication over the internet. Basically, it takes audio signals and turns them into digital transmission data, which can be sent from one point to the other via the internet.
By using VoIP, users can make calls without a physical telephone line by just using their internet connection. A lot of VoIP providers also offer additional features such as mobile integration, video conferencing, and instant messaging. Here are some advantages of VoIP over ISDN:
- VoIP is far more cost effective than ISDN. Not only is the installation cost considerably lower but it’s 40 to 90 percent cheaper to make calls.
- With VoIP, users can enjoy flawless quality of calls and the rate of call failures is quite negligible.
- VoIP can be set up, customized, and scaled easily. Takes seconds to set up.
- VoIP is highly flexible as it’s not tied to a geographical location.
- By using VoIP, you just need to plug into an existing internet connection with no external sources needed.
- VoIP comes equipped with sophisticated call features such as auto attendants, skill-based routing, extensions, call analytics, and more.
2. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Trunking
SIP trunking uses SIP-enabled PBX (Private Branch Exchange) systems to make and receive phone calls over an internet connection. It provides greater flexibility and scalability compared to traditional phone lines. It also has many advantages over ISDN such as:
- Save costs by allowing consolidation of technologies for unified communications.
- Higher security by storing data on on-premises and centralized systems.
- Transmits voice, video, and text data and provides a multimedia experience.
- Advanced cloud application integration capabilities.
3. Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange (IP PBX)
IP PBX System enables businesses to manage their phone systems over the internet and allows for integration with other communication tools, such as video conferencing and messaging, streamlining operations. Compared to ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network), IP PBX offers:
- Cost savings by leveraging existing internet infrastructure
- Eliminates the need for separate phone lines
- Supports advanced features like call routing, voicemail-to-email, and remote access
- Enhances productivity and customer service
- Excellent adaptability and modern functionality
4. Wireless Broadband
Wireless broadband technologies such as 4G LTE and 5G offer fast and reliable internet access without the need for physical cables. Wireless broadband can be an excellent option for businesses in remote or rural areas where wired infrastructure may be lacking.
Additionally, wireless broadband can provide a backup or redundancy option for businesses that require reliable internet connectivity. Here are some benefits of wireless broadband over ISDN:
- Greater mobility and flexibility compared to ISDN.
- Eliminates the need for physical cables, providing easier installation and setup.
- Can be quickly deployed in remote or temporary locations where wired infrastructure is impractical.
- Offers reliable connectivity even in areas with poor or limited wired infrastructure.
- Enables rapid expansion of network coverage without the need for extensive infrastructure investments.
5. Fiber Optic Internet
Fiber optic internet delivers ultra-fast speeds and high bandwidth capabilities, making it an ideal choice for businesses with demanding data requirements. Fiber optic internet offers superior performance and reliability compared to traditional copper-based technologies like ISDN.
While fiber optic infrastructure may not be available in all areas, its widespread deployment continues to expand, providing more businesses with access to high-speed internet connectivity. It has the following advantages over ISDN:
- Offers significantly higher data transfer speeds compared to ISDN.
- Provides greater reliability and stability for voice and data communication.
- Highly scalable and can easily accommodate growing bandwidth demands.
- Extremely immune to electromagnetic interference.
- Enables longer transmission distances without signal degradation compared to ISDN.
In Conclusion,
Former Google’s CEO Larry Page once said, “Especially in technology, we need revolutionary change, not incremental change.” In the 80s, ISDN brought a revolutionary change in the field of telecommunications. Four decades later, it is set to be phased out and replaced by new technologies such as VoIP, SIP, and high-speed broadband.
ISDN will not be in existence after 2025. And businesses that still use the network must start looking for various alternatives out there. At HoduSoft, we have helped a wide range of businesses of various types and sizes switch to the right network.
If you are looking to switch over from ISDN to VoIP, SIP, or IP PBX systems, then you may want to consider the experience and expertise of a service provider that has a robust track record. Contact us today for a free demo.