What is PSTN – A Complete Guide
Do you know the first commercial telephone service in the world began in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada on June 20, 1877? This service was based on the patent Alexander Graham Bell received in 1876. On 10th March 1976, Bell spoke the first words via a telephone. And, these words were, “Mr. Watson, come here, I want to see you”.
These words have been memorialized in history and the above-mentioned date is marked as the official date of the discovery of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell. That’s how we got a great communication system. Since its invention, the telecommunications system has evolved to a great extent.
Telephone technology evolved swiftly after the first commercial services emerged. It evolved with underground copper wires, telephone cables under the sea, communication satellites, and a digital core PSTN network. After the evolution of the internet, there has been a steady decline in the use of PSTN. In this blog, we will disclose detailed information related to PSTN. You will get to know everything about PSTN and the key reasons for the worldwide decline in its usage. Also, we will talk about some of the modern alternatives to PSTN.
We will cover the following topics:
What is PSTN?
PSTN stands for Public Switched Telephone Network. Also known as the traditional circuit-switched telephone network, this legacy platform has been in use since the late 1800s. Several businesses and households relied on this communication platform to connect with anyone throughout the world. In fact, PSTN phones were widely accepted as a standard form of communication. People know PSTN by several names such as:
- PSTN
- Landlines
- Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS)
- Fixed-line telephones
This platform encompasses all the switched telephone networks throughout the world that are run by local, national, or international carriers. These networks offer the required infrastructure and services for public telecommunication.
Let’s go a little deeper into the history of PSTN to know more about this platform.
The history of PSTN starts in the year 1875 when Alexander Bell established the American Bell Telephone Company. After a year, as mentioned above in the blog, Alexander Bell had the first voice transmission over the wire, which was patented as the first advancement in telegraphy.
The first voice transmission was carried out using a ring-down circuit. This transmission doesn’t have the facility to dial numbers. Instead, physical wires were connected between two devices. To communicate with a person, the user had to whistle to draw the person’s attention to the other side. Later on, Alexander introduced a calling bell system, which made signaling much easier for the receiver of the call.
Over time with the advancement in technology, the demand for a phone in every household increased. However, it was not possible to install several wires between buildings. To resolve this issue, Bell developed another method that could map any phone to another without a direct connection. This method was named a ‘Switch’. This is when the role of a control center came into the picture. Whenever a person needs to call another person, the call would first reach a centralized office. The operator at the centralized office then connects the wires in the switch and routes the call to its correct destination.
With further advancements in technology, the switches used by operators have been replaced with analog and then digital switches. This digital progression resulted in improved sound quality and long-distance coverage. With digital evolution, PSTN also released many new features like:
- Call forwarding
- Call waiting
- Conference calling
With the launch of Internet and broadband internet services, PSTN became outdated. Presently, there are just 972 million fixed-line telephone subscriptions in use globally, which is probably the lowest count so far.
How does PSTN work?
A PSTN is a blend of telephone networks used globally. These telephone networks include:
- Telephone lines
- Cellular networks
- Fiber optic cables
- Switching centers
- Satellites
- Cable systems
A PSTN allows users to make landline telephone calls to one another. It is made up of switches at centralized points on the network. These switches play an important role of nodes, enabling communication between two points on the network. Let’s break down how PSTN lines actually work in various steps:
- As soon as you dial a number, your phone starts converting sound waves (your voice) into electrical signals.
- Once the sound waves convert into electrical signals, these signals are transmitted to a terminal via cables.
- The electrical signals are then transmitted by the terminal to the central office or local exchange.
- Once the central office obtains the electrical signals, they are sent to the right destination through cables in the form of light pulses.
- As soon as the call reaches its destination, light pulses are converted back to electrical signals and directed to the correct terminal.
- When the electrical signals reach the terminal, the terminal will route the call to the right phone number.
- Finally, the phone receives the electrical signals, where it covers these signals back into sound waves. This allows instant communication between you and the person you want to talk with.
Don’t get confused with so many steps involved in reaching a particular destination over a call. It only takes a few seconds to allow a connection.
Structure of PSTN
The traditional PSTN has a hierarchical architecture and a star structure. Under this structure, the individual PSTN lines are connected to a local exchange. These lines facilitate communications with trunk exchanges, main exchanges, and central exchanges. As far as the area codes are concerned, it works in the following manner:
- The lines within a local exchange usually have the same area code.
- If a user needs to call a number outside the local exchange, it becomes essential to add the area code.
- For making international calls, it is important to dial the country code.
Now that you know what is a PSTN phone line, you must understand what components a telephone system model is composed of. Well, a telephone system model usually comprises the following components:
- Telephone: Telephone of the subscriber/end-user.
- End office: It is a local central office that is directly connected to the end-user at a distance of 1 to 10 km.
- Local loop: It is simply a two-way connection between the telephone and the end office.
- Toll office: Toll offices are the switching centers, also known as end offices, located within the same local area.
- Toll connecting trunk: These are the lines that connect end offices with toll offices.
- Intermediate switching offices: These are interconnected non-hierarchical switching offices that connect toll offices.
Inter toll trunk: These are very high bandwidth channels that connect with two toll offices via intermediate switching offices.
VoIP is one of the best alternatives to PSTN. Emerged in the mid-2000s, VoIP technology has emerged as a legitimate alternative to PSTN. VoIP telephony is an entirely cloud-based system in which calls are routed via the internet. With hosted systems, users need not pay additional maintenance charges. Besides, each user will have their own dedicated line. This telephony system is suitable for all types of companies from SMEs to multi-national enterprises. Basically, if you are looking for a fixed-cost business telephony system with extra functionality, high call quality, and lower call charges then VoIP is the right choice.
Why Businesses Must Upgrade to VoIP?
There are several businesses that are still using their existing PSTN phones. No doubt, PSTN is a reliable system as businesses can use it even during times of emergencies in case of a power cut. Even employees already know how to make and receive PSTN calls. They know how to make use of some of the advanced enterprise features available on the PSTN line for better call management. Due to all these factors, many companies find it quite troublesome to make a switch to VoIP. However, in reality, upgrading to VoIP takes very less time and money as compared to any other enterprise technology. Based on the size of your business, it may take just a few hours to get started.
In today’s time, hosted VoIP is a dominant business model which requires very little initial investment. To opt for this model, businesses may require purchasing VoIP phones and upgrading some of their network equipment. Moreover, the process of making calls is similar to VoIP which eliminates the need to retrain the users. Once the VoIP system is ready to use, anyone can handle the calls.
It may take some time for users to become completely familiar with the advanced functionalities of the VoIP system. But they can easily learn these functionalities as they go along. Most VoIP solution providers also provide manuals, databases, user guides, and seminars to help users learn various functionalities easily in no time. It is now understood that by making a switch to VoIP, businesses can enhance their productivity as well as collaboration without making a huge investment.
Let’s have a look at some of the key benefits of VoIP
- Cost savings: One of the key benefits of VoIP is cost savings. Various areas that contribute to low costs when using VoIP systems include- free calls between employees, low-cost monthly/annual plans, low international calling rates, no maintenance charges, no requirement to budget for periodic upgrades to PBX equipment, etc.
- Scalability: Scalability is another main advantage of the VoIP system. Businesses just have to pay for what they use. They can easily add or remove resources from their calling plan as per their requirements. They don’t have to pay for the lines and numbers that they are not using. Moreover, scaling up or down takes only a few hours, which allows businesses to meet their demand easily and accurately.
- Requires a single IP network: Unlike other business phone systems that need to maintain two different networks for communication (PSTN and IP), VoIP allows voice communication over the IP network, enabling better alliance and convergence.
Free value-added features: Traditional phone service providers usually charge for additional features. Users can get these features for free with a VoIP business phone system. Besides, many older technologies like PSTN do not support many new features.
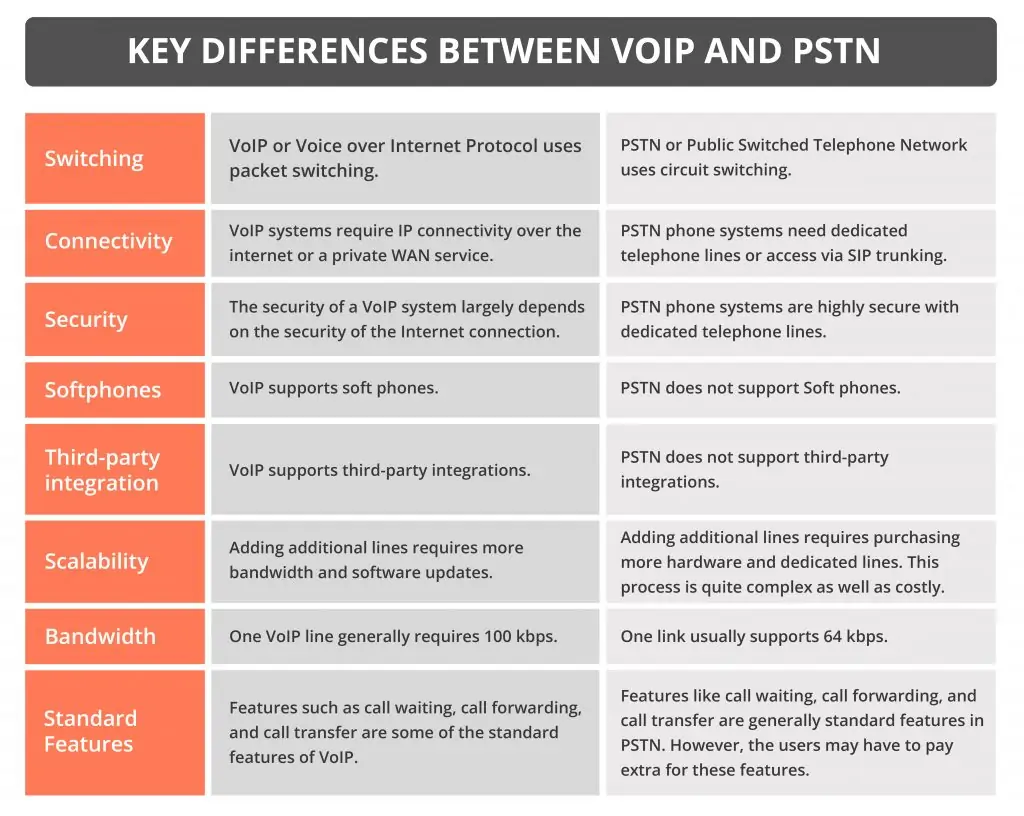
Let’s look at the key differences between VoIP and PSTN based on various features:
Since both PSTN and VoIP technologies are different, there is no better or worse choice. Based on the key needs of your business as well as the features and benefits that these technologies provide, you can easily determine which technology will be the better fit for your company.
Conclusion:
No doubt PSTN has several advantages. Many businesses are using PSTN lines as these are highly reliable, especially during a power outage. Besides, its service and call quality are quite stable. However, if you need to grow your business in this technologically advanced business world, you must switch to VoIP. VoIP also comes with many advantages. Mobility is one of the key advantages of this system which allow users to take their VoIP device anywhere as per their requirement. Besides, it’s a cost-effective and feature-rich system.